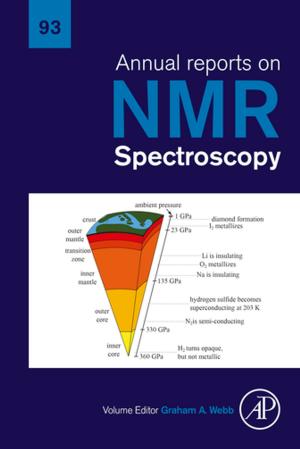
The Role of Global Air Pollution in Aging and Disease
Reading Smoke Signals
Nonfiction, Health & Well Being, Medical, Specialties, Geriatrics, Internal Medicine, General| Author: | Caleb E. Finch | ISBN: | 9780128131039 |
| Publisher: | Elsevier Science | Publication: | January 21, 2018 |
| Imprint: | Academic Press | Language: | English |
| Author: | Caleb E. Finch |
| ISBN: | 9780128131039 |
| Publisher: | Elsevier Science |
| Publication: | January 21, 2018 |
| Imprint: | Academic Press |
| Language: | English |
Global Air Pollution in Aging: Reading Smoke Signals is a complete reference connecting environmental pollution research to the human aging process. Since 1800, lifespans have more than doubled as infections declined and medicine improved. But the 20th century introduced a new global scourge of air pollution from fossil fuels with the potential to damage arteries, hearts and lungs that has been related to chronic exposure of air pollution from fossil fuels. Risk areas of study include childhood obesity, brain damage associated with air pollution, increased risk for autism in children and dementia in older adults.
In humans and animals, air pollution stimulates chronic inflammation in different organs, and genetic vulnerability to air pollution is being recognized, particularly for carriers of the Alzheimer risk gene ApoE4.
- Connects environmental pollution research to the human aging process
- Raises new issues relevant to the controversies on air pollution and global warming, challenging assumptions that lifespan will continue to increase in the 21st Century
- Examines the burden of air pollution to disadvantaged populations, with anticipated greater impact in developing countries which rely on fossil fuels for economic development in future decades
Global Air Pollution in Aging: Reading Smoke Signals is a complete reference connecting environmental pollution research to the human aging process. Since 1800, lifespans have more than doubled as infections declined and medicine improved. But the 20th century introduced a new global scourge of air pollution from fossil fuels with the potential to damage arteries, hearts and lungs that has been related to chronic exposure of air pollution from fossil fuels. Risk areas of study include childhood obesity, brain damage associated with air pollution, increased risk for autism in children and dementia in older adults.
In humans and animals, air pollution stimulates chronic inflammation in different organs, and genetic vulnerability to air pollution is being recognized, particularly for carriers of the Alzheimer risk gene ApoE4.
- Connects environmental pollution research to the human aging process
- Raises new issues relevant to the controversies on air pollution and global warming, challenging assumptions that lifespan will continue to increase in the 21st Century
- Examines the burden of air pollution to disadvantaged populations, with anticipated greater impact in developing countries which rely on fossil fuels for economic development in future decades