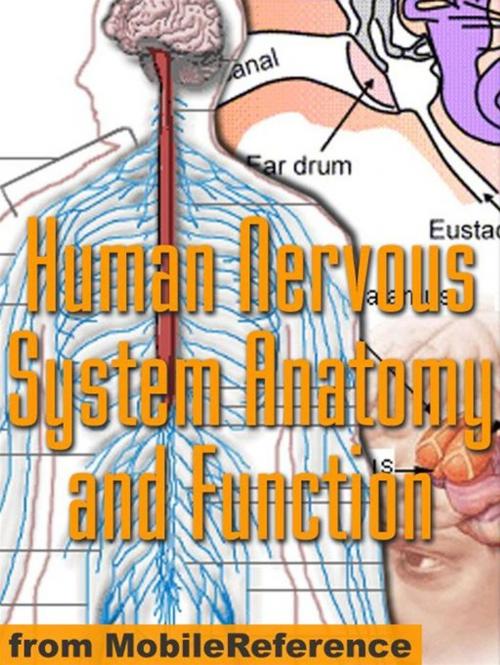
Human Nervous System Anatomy And Function Study Guide (Mobi Medical)
Nonfiction, Reference & Language, Study Aids, Reference, Health & Well Being, Medical| Author: | MobileReference | ISBN: | 9781605010847 |
| Publisher: | MobileReference | Publication: | January 1, 2010 |
| Imprint: | MobileReference | Language: | English |
| Author: | MobileReference |
| ISBN: | 9781605010847 |
| Publisher: | MobileReference |
| Publication: | January 1, 2010 |
| Imprint: | MobileReference |
| Language: | English |
Human Nervous System Anatomy and Function Study Guide Audience:Intended for everyone interested in human nervous system, particularly undergraduate and graduate life science students, medical students, nursing students, physician assistants students, and physical therapy students.FEATURES:- Fully illustrated Written in clear, concise format. Difficult concepts are explained in simple terms. - Access the guide anytime, anywhere - at home, on the train, in the subway. - Hyperlinked table of contents- Add Bookmarks - Designed for optimal navigation on electronic devices with a small screen Use your down-time to prepare for an exam. - Always have the guide available for a quick reference.TABLE OF CONTENTS:I. Cells of the Nervous SystemNeuron: Overview Axon Dendrite Apical dendrite Dendritic spine Synapse Neuromuscular junction Afferent nerve Efferent nerve Sensory nerve Motor nerveTypes of neurons: Pyramidal cell Betz cell Purkinje cell Muscle spindle Golgi organ Motor neuron Sensory neuronGlial cell: Overview Astrocyte Oligodendrocyte Schwann cell MyelinII. Regional AnatomyAnatomical terms: Position Direction MotionNervous System Organization: Overview Brain Spinal cord Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous systemBrain Stem external anatomy: Brain Stem Medulla oblongata Pons MidbrainBrain Stem nuclei: Olivary body Cochlear nuclei Superior olivary nuclei Inferior colliculi Medial geniculate nuclei Superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Reticular formation Raphe nuclei Locus ceruleus Pedunculopontine nucleus Midbrain nucleiCranial nerves: Overview I olfactory II optic III oculomotor IV trochlear V trigeminal V1 ophthalmic V2 maxillary V3 mandibular VI abducens VII facial VIII vestibulocochlear (cochlear, vestibular) IX glossopharyngeal X vagus XI accessory XII hypoglossalCerebellum: Overview Development and evolution Anatomy Blood supply Dysfunction Theories about cerebellar function Purkinje cellDiencephalon: Overview Thalamus : Medial geniculate nuclei Lateral geniculate nucleus Thalamocortical loop Hypothalamus Epithalamus : Pineal gland Habenula Subthalamus Pituitary gland : Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary Other : Third ventricle Interventricular foramina Optic chiasm Subfornical organVentricular system: Overview Lateral ventricles Interventricular foramina Third ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Fourth ventricle Central canal Choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluidCorpus striatum: Overview Basal ganglia Striatum Putamen Caudate nucleus Nucleus accumbens Globus pallidus Subthalamic nucleus Substantia nigra.....III. Major SystemsVisual system: Overview Eye Rods Cones Rods vs. Cones Optic nerve Optic chiasm Optic tract Lateral geniculate nucleus Optic radiation Visual cortexand much more..
Human Nervous System Anatomy and Function Study Guide Audience:Intended for everyone interested in human nervous system, particularly undergraduate and graduate life science students, medical students, nursing students, physician assistants students, and physical therapy students.FEATURES:- Fully illustrated Written in clear, concise format. Difficult concepts are explained in simple terms. - Access the guide anytime, anywhere - at home, on the train, in the subway. - Hyperlinked table of contents- Add Bookmarks - Designed for optimal navigation on electronic devices with a small screen Use your down-time to prepare for an exam. - Always have the guide available for a quick reference.TABLE OF CONTENTS:I. Cells of the Nervous SystemNeuron: Overview Axon Dendrite Apical dendrite Dendritic spine Synapse Neuromuscular junction Afferent nerve Efferent nerve Sensory nerve Motor nerveTypes of neurons: Pyramidal cell Betz cell Purkinje cell Muscle spindle Golgi organ Motor neuron Sensory neuronGlial cell: Overview Astrocyte Oligodendrocyte Schwann cell MyelinII. Regional AnatomyAnatomical terms: Position Direction MotionNervous System Organization: Overview Brain Spinal cord Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous systemBrain Stem external anatomy: Brain Stem Medulla oblongata Pons MidbrainBrain Stem nuclei: Olivary body Cochlear nuclei Superior olivary nuclei Inferior colliculi Medial geniculate nuclei Superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Reticular formation Raphe nuclei Locus ceruleus Pedunculopontine nucleus Midbrain nucleiCranial nerves: Overview I olfactory II optic III oculomotor IV trochlear V trigeminal V1 ophthalmic V2 maxillary V3 mandibular VI abducens VII facial VIII vestibulocochlear (cochlear, vestibular) IX glossopharyngeal X vagus XI accessory XII hypoglossalCerebellum: Overview Development and evolution Anatomy Blood supply Dysfunction Theories about cerebellar function Purkinje cellDiencephalon: Overview Thalamus : Medial geniculate nuclei Lateral geniculate nucleus Thalamocortical loop Hypothalamus Epithalamus : Pineal gland Habenula Subthalamus Pituitary gland : Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary Other : Third ventricle Interventricular foramina Optic chiasm Subfornical organVentricular system: Overview Lateral ventricles Interventricular foramina Third ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Fourth ventricle Central canal Choroid plexus Cerebrospinal fluidCorpus striatum: Overview Basal ganglia Striatum Putamen Caudate nucleus Nucleus accumbens Globus pallidus Subthalamic nucleus Substantia nigra.....III. Major SystemsVisual system: Overview Eye Rods Cones Rods vs. Cones Optic nerve Optic chiasm Optic tract Lateral geniculate nucleus Optic radiation Visual cortexand much more..